LASIK Surgery
LASIK (laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis), is the most popular refractive surgical procedure. In this procedure, a laser is used to permanently change the shape of the cornea (the clear covering on the front of the eye) to correct common vision problems such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia. This improves vision and reduces a person's need for glasses or contact lenses.
LASIK uses an excimer laser (an ultraviolet laser) to remove a thin layer of corneal tissue, giving the cornea a new shape, so that light rays are focused clearly on the retina. In the case of a nearsighted person, the goal of LASIK is to flatten the too-steep cornea; with farsighted people, a steeper cornea is desired. LASIK can also correct astigmatism by smoothing an irregular cornea into a more normal shape.
LASIK is an outpatient surgical procedure with no need to stay at the surgery center overnight as it will take 10 to 15 minutes to perform for each eye. The procedure is done while the patient is awake, but the patient may request mild sedation. The only anesthetic used is eye drops that numb the surface of the eye. LASIK can be done on one or both eyes during the same session.
How to Prepare for LASIK Eye Surgery?
Before LASIK eye surgery, the eye surgeon will evaluate the patient’s medical history and perform a full eye examination, including measuring corneal thickness, refraction, corneal mapping, eye pressure, and pupil dilation. Afterward, the surgeon will discuss what to expect during and after the procedure.
On the day of the surgery, eat a light meal before going to the doctor and take all prescribed medications, if any. Do not wear eye makeup, creams, perfumes or lotions on the day before and the day of surgery, or have any bulky hair accessories that will interfere with positioning head under the laser.
Contact lenses shouldn't be worn for at least three days prior to the evaluation. In the case of, rigid gas permeable contact lenses, they should not be worn for at least three weeks before. Patients should arrange for a ride home from the place of surgery, as their vision might be blurry.
Refraction Test
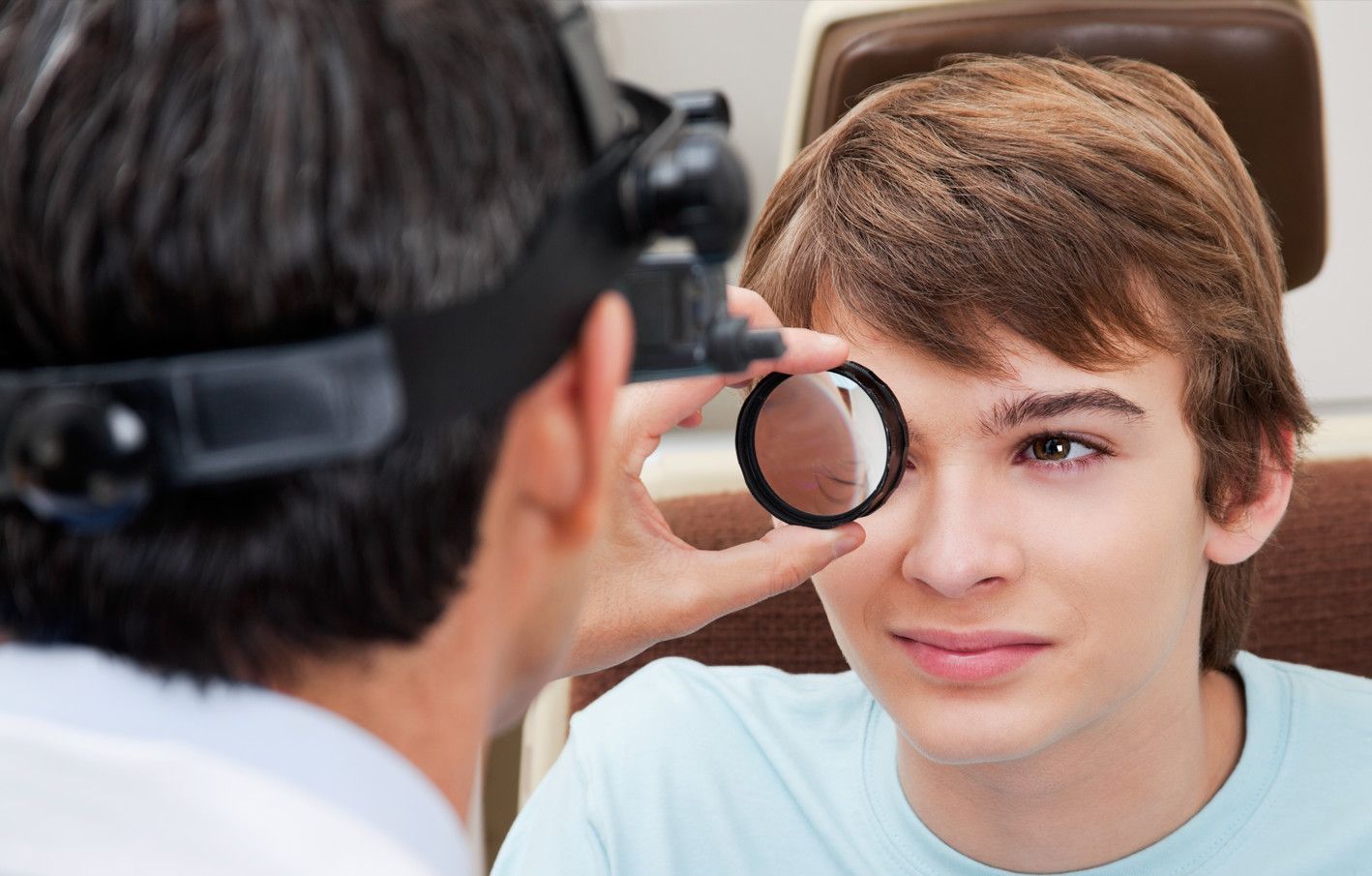
A refraction test, also called a vision test, is usually performed as a part of a routine eye examination. The purpose of this test is to determine if a person has a refractive error which would then mean the patient would need glasses or contact lenses.
What Is The Normal Value for Refraction Test?
A value of 20/20 is normal (optimum) vision. This means that individuals who have 20/20 vision are able to read letters that are 3/8-inch (1 centimeter) tall from 20 feet (6 meters) away. The normal uncorrected vision (without glasses or contact lenses) refractive error is zero (plano). Individuals who don’t have 20/20 vision, have what is called a refractive error. A refractive error means that the light is not bending properly when it passes through the lens of the eye. The refraction test will tell the doctor what prescription lens should be used in order to have 20/20 vision.
For people over age 40 who have normal distance vision but difficulty with near vision, a refraction test with a small type size is used to determine normal near vision and the correct power of reading glasses.
How Is The Refraction Test Performed?
The test is performed by having the patient seated in a chair that has a special device (called a phoropter or refractor) attached to it. The patient looks through the device and focuses on an eye chart 20 feet (6 meters) away. The device contains lenses of different strengths that can be moved into the patient’s view. The test is performed one eye at a time. If the patient is wearing contact lenses, they should be removed before the test.
In case the final vision is less than 20/20 even with lenses, then there is probably another non-optical problem with the eye. The vision level achieved during the refraction test is called the best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA).
What Are The Causes of Abnormal Refraction Test Results?
Abnormal results may be due to:
Astigmatism (abnormally curved cornea causing blurred vision)
Hyperopia (farsightedness)
Myopia (nearsightedness)
Presbyopia (inability to focus on near objects that develop with age)
Other conditions under which the test may be performed:
Corneal ulcers and infections
Loss of sharp vision due to macular degeneration
Retinal detachment (separation of the light-sensitive membrane (retina) in the back of the eye from its supporting layers)
Retinal vessel occlusion (blockage in a small artery that carries blood to the retina)
Retinitis pigmentosa (an inherited disorder of the retina)
There is an art to refraction and the optometrist will always answer the patient’s questions and as well as discuss their findings. Based on the results of the refraction test, they can determine the amount of myopia, hyperopia or astigmatism.
Amblyopia
Amblyopia, also known as a “lazy eye”, is described as a reduced vision in one eye compared to the other. There are some rare forms of amblyopia that involve both eyes. Amblyopia is the most common cause of partial or total blindness in one eye in children.
The term lazy eye is misleading because the eye is not actually lazy. In fact, it is a developmental problem in the nerve connecting the eye to the brain, affecting the brain’s ability to use both eyes together. It is not a problem in the eye itself, but in the brain which actively ignores the visual input from the misaligned eye, leading to amblyopia in that eye.
In addition to poor visual acuity, people with amblyopia are more prone to having difficulties with depth perception, eye movements related to reading, and visual decision making while driving.
What Are The Causes of Amblyopia?
Amblyopia develops in childhood due to:
Significant differences in the prescription (refractive) status between the two eyes due to nearsightedness, farsightedness or astigmatism;
Constantly misaligned eyes or crossed eyes (strabismus);
An obstruction of vision in early childhood i.e. cataract, ptosis (droopy eyelid)
It is important to note that, because amblyopia is typically a problem of infant vision development, symptoms of the condition can be difficult to detect. Symptoms may include noticeably favoring one eye over the other, an eye turn (either upward-downward outward or inward) or a tendency to bump into objects on one side.
The best way to identify children who are at risk for or already have amblyopia is by performing comprehensive eye examinations.
How Is Amblyopia Treated?
Amblyopia can be treatable at any age, although the earlier the problem is found and treated, the more successful the outcomes tend to be.
Types of Daily Contact Lenses
Wearing contact lenses gives patients the flexibility and freedom to live life to the fullest, without some of the difficulties presented by wearing glasses. Many people who choose contact lenses do so because they don’t like the way that glasses look or feel, or because wearing glasses compromises their ability to perform certain tasks or activities, such as sports or jobs that require the use of safety goggles.
There are lots of different contact lenses to choose from, with two of the most popular being daily disposables and toric lenses.
Disposable Lenses
As their name suggests, these daily contact lenses are disposable. This means that they can and should be discarded at the end of each day rather than re-worn. Disposable lenses do tend to be a little more expensive than some repeat-wear varieties, but the benefits usually outweigh the cost.
Some of the advantages of choosing daily disposable contact lenses include:
You don’t have to clean them, which saves patients a great deal of time and hassle. It also helps save money in terms of the ongoing cost of cleaning solution.
Disposable lenses are also great for people with eye allergies. This is because with ordinary lenses, there’s an opportunity for deposits and microorganisms to build up. With daily disposables, allergens have less chance to attach themselves to the lenses and cause irritation and other allergy symptoms.
You don’t need to schedule regular replacements either, which makes wearing contact lenses easier on your schedule.
Disposable contact lenses are particularly good for people who have busy lives and are likely to cut corners when it comes to caring for their eyes or contacts since there is no cleaning or maintenance required.
Daily disposable contact lenses are available in a wide range of prescriptions, including those for patients with nearsightedness and farsightedness. Your eye doctor will be able to advise you if you are a candidate for disposable contact lenses.
Toric Lenses
Toric contact lenses are recommended for patients who have a refractive eye problem called astigmatism. Patients with astigmatism have corneal abnormalities that cause the refraction of the eye to be different between the vertical and horizontal planes, causing blurred vision and difficulty seeing fine details. Toric contact lenses are shaped in a particular way that creates the different focusing powers needed in each part of the lens to correct your vision. For this reason, it’s essential that Toric lenses are placed into the eyes in the correct position.
Fortunately, manufacturers design Toric lenses with features that help them to stay in place, including:
Thin/thick zones
Creating areas of the lens that are thicker or heavier which helps secure it in position
An area where the bottom of the lens is slightly cut off
To keep them stable, Toric lenses are a little firmer than conventional soft lenses. This means that some patients can find them a little less comfortable, but the superior vision they obtain outweighs this. Your eye doctor will be able to advise you if you are a good candidate for Toric contact lenses and which variety would best suit you.
To find out more about daily contact lenses, speak to our friendly and knowledgeable team.
Keratoconus and Your Treatment Options
Keratoconus is a terrifying diagnosis to those that have experienced it. To compound issues, many patients complain that they had poor initial treatment due to a lack of understanding about the disease. If proper treatment is not achieved, individuals may experience a rapid deterioration in their ability to see. This leads to a reduced quality of life. You can reduce the stress related to a keratoconus diagnosis and increase the benefits of treatment by understanding your treatment options.
Understanding Keratoconus
Keratoconus is an eye disease that causes the cornea to thin and bulge. This bulge generally takes on the appearance of a cone. As light enters the eye, it becomes distorted by the cone causing vision abnormalities.
Modern research is connecting keratoconus with an enzyme imbalance in the cornea. This imbalance leaves the eye susceptible to oxidative free radicals. Keratoconus has also been linked to UV damage, excessive eye rubbing, poorly fitting contacts, and chronic eye irritation.
Treatment Options
While your eye professional will have the best understanding of what treatment option is right for you, we have compiled ten of the most common treatments here.
Corneal Cross-linking (CXL) – There are two different types of this procedure, but they both introduce riboflavin to the cornea in order to strengthen the corneal tissue and stop the bulging from progressing.
Custom Soft Contact Lenses – Soft contacts are generally more comfortable to wear than gas permeable lenses. Recently, some contact companies have been able to create a contact specifically to correct the issues related to mild and moderate cases of keratoconus.
Gas Permeable Contact Lenses – Gas permeable lenses are a hard contact lens that physically forces the eye to adhere to the lens shape. This allows for the correction of keratoconus. The fit is often time-consuming and may take several different lenses to achieve the proper fit.
Piggybacking Contact Lenses – This method is used for individuals who require a gas permeable lens but cannot tolerate wearing rigid contacts. Piggybacking utilizes a soft lens placed on the eye first, and then a gas permeable lens is placed over the top. This offers the comfort of soft contacts with the rigidity and clarity of the gas permeable lenses.
Hybrid Contact Lenses – Hybrid contact lenses were designed specifically for keratoconus. This technology blends a rigid contact lens center with a softer edge, or skirt, of the contact
Scleral and Semi-Scleral lenses – These lenses are gas permeable lenses but cover a larger area of the eye than a standard rigid lens. These lenses don’t put pressure onto the cone shape of the eye. The reduced pressure results in a more comfortable fit for patients.
Prosthetic Lenses – This lens is used specifically for patients that have very advanced keratoconus and have ruled out other options. The advanced scleral lens also doubles as a protective prosthetic shell. There are special requirements to qualify for this lens though, so check with your eye care professional if this is an option for you.
Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical Coherence Tomography is a non-invasive imaging test that may be performed as a standard part of your regular, comprehensive exams, or you may be able to request this test as an addition to your usual exam.
Optical Coherence Tomography uses light waves to take cross-section images of your retina, which is the area of light-sensitive cells at the back of your eye that is responsible for receiving light and transmitting it into messages that are sent up to the brain. The technology behind OCT enables your eye doctor to see each of the different layers that make up the retina. By being able to see these and measure them, they can obtain a much clearer picture of the overall health and condition of your eyes.
Why are Optical Coherence Tomography scans important?
When you choose to have an OCT scan at fairly regular intervals, such as during your normal comprehensive eye exams, your eye doctor can compare newer results to previous ones. This helps them to build up a picture of the health of your eyes, and spot any changes which may be concerning, early, before they cause symptoms or have a permanent effect on your vision.
Anyone can have an OCT scan, but they are particularly recommended for patients over the age of 25 who are concerned about the health of their eyes, or who are at risk of or already have diabetes, glaucoma or a family history of eye disease. This is because they can be used to spot the early signs of a range of eye diseases, including glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, disorders of the optic nerve and more – even before you realize that you are affected.
What happens during an Optical Coherence Tomography scan?
An OCT scan is a quick, painless experience. To prepare you, your eye doctor may require you to have eyedrops that will dilate your pupils and make it easier to see your retina. This means that the scanner will get clearer, more concise images. You’ll be asked to sit in front of the OCT machine where you will rest your head against a support to help you sit perfectly still. As you stare ahead, the equipment will perform the scan of your eyes. There is no contact with your eyes whatsoever, you will just need to sit still, with your eyes open as much as possible during the process, which usually takes less than 10 minutes. The images will be sent digitally to your eye doctor for them to assess immediately and stored digitally on your personal record.
There’s no downtime after an OCT scan, but if you have had your eyes dilated you may find that you are particularly sensitive to light for a few hours afterwards. This occurs because the pupils remain wider and therefore able to let more light in that usual.
If you would like to find out more about Optical Coherence Tomography, don’t hesitate to speak to our professional eyecare team.
Optikam
Eye care professionals use Optikam’s technology to capture more than 3 million eyewear measurements every year. The OptikamPad iPad app is a total dispensing solution that enables eye care professionals to successfully assist patients at all stages of the eyewear dispensing process, providing them with a unique and custom patient experience.
Optikam Posture Devise (OPD)
You may be surprised to learn that wearing glasses can and likely will affect your posture. Glasses lenses are most accurate when you look directly through their center. This means if your glasses are sitting too low or have slipped down your nose, you may find that you are subconsciously tilting your head back and this can affect your overall posture.
Optikam’s OPD measurement device is a cutting-edge tool that obtains eyewear measurements that take into account how the frame will be worn by patients, enabling the fit to be customized to their individual parameters. The ten measurements taken into account when determining each patient’s position of wear include:
Monocular pupillary distance
Multifocal seg heights
Pantoscopic tilt
Rear vertex distance
Wrap (face form tilt)
Near pupillary distance
This results in frames that not only look fantastic, but that also fit perfectly, remaining both comfortable and stable on the face without you needing to adopt an unnatural posture. The measurements obtained by the Optikam OPD measurement tool are immediately visible on your eye doctor’s tablet so that they can recommend which alterations to the frames are needed to ensure that the frames fit with precision and gives you the best visual experience.
Benefits of OptikamPad and Optikam OPD
Traditionally, the process of a comprehensive eye exam, choosing frames and fitting glasses requires fairly close contact with your eye doctor or other eye care professionals. However, with social distancing being a new process variable, many patients are looking for more virtual options. Fortunately, OptikamPad makes it possible for optical stores to dispense eyeglasses with minimal human contact. This is because the OptikamPad can take measurements from a further distance or even through plexiglass screens. It can even be placed on a stand and the app operated using a Bluetooth mouse, putting even greater distance between your eye care professional and you.
If you would like to find out more about Optikam OPD and OptikamPad, our knowledgeable team would be delighted to help. Please contact us with any questions or to schedule an appointment.
Sports Vision
Sports vision is a growing niche in the eyecare industry, helping athletes improve their performance skills through the enhancement of visual skills. While regular eye exams are important for checking the health of your eyes and your visual acuity (how clearly you can see a still object at different distances), sports vision testing is recommended for anyone who takes their athletic performance seriously.
Visual skills needed for sports performance
There are several key visual skills that are enhanced through sports vision programs for athletes that aim to achieve their optimal sports performance, these include:
Dynamic visual acuity: this refers to the patient’s ability to see objects clearly while in motion. This is exceptionally important as hand-eye coordination and reflex reactions are essential for success in most sporting activities.
Contrast sensitivity: good contrast sensitivity is needed to determine the difference between an object and its surroundings. Contrast sensitivity is particularly important in situations where there may be low light, fog or glare that could diminish the natural contrast between objects and backgrounds.
Eye tracking: this refers to the ability to follow a fast-moving object, such as a ball or puck.
Switching eye focus: athletes need to be able to change their focus quickly and accurately from one distance to another.
Binocular vision skills: also known as eye teaming skills, these skills determine how well your eyes work with one another to produce a single, clear image.
Processing speed: visual processing speed is defined as the amount of time it takes to make a correct judgement about a visual stimulus – for example, how fast a ball is travelling towards them.
Peripheral awareness: athletes also need to be able to be aware of what is happening at the edges of their vision while also concentrating on a fixed object in front of them.
Sports vision testing can enable your eye doctor to spot any weaknesses that you may have in any of these key visual skills. By identifying them, it is possible for you to undergo treatment to overcome theses issues and meet your specific goals that will ultimately enhance your overall athletic performance. This is known as sports vision training.
What’s involved in sports vision training?
Sports vision training refers to a personalized treatment plan that is designed to train the brain to achieve maximum efficiency in the way that it receives, processes, and responds to visual input. Exactly what is involved in your sports vision training will depend on your athletic activity and the visual skills that your eye doctor identifies for improvement after comprehensive sports vision testing. Your treatment program will use a variety of tools, techniques, and exercises. You may also be asked to complete some exercises at home to further enhance your progress. With sports vision training, the ultimiate goal is for athletes to continue to see faster and clearer, giving them a distinct competitive edge.
For more information about sports vision and how it can benefit amateur and professional athletes, please contact our team.
Overview of Common Ocular Diseases
Both optometrists and ophthalmologists treat many common types of ocular disease. However, for the best outcome, it’s important to see an eye doctor regularly. They can identify any issues before they become serious problems.
Fortunately, they can treat all of the diseases mentioned below, and in some cases, you can do certain things to prevent them from developing. Look at the most recent statistics, and you’ll see why good eye health care matters.
Currently, more than 4.2 million people in the U.S. alone over the age of 40 are partially blind or have poor visual acuity. Although a lot of things cause these problems, the ocular diseases listed below are the most common.
Macular Degeneration
This is commonly referred to as “age-related macular degeneration” because it affects seniors. Not only does it cause blurriness and distortion but left untreated, individuals lose their central vision. In other words, they are unable to see anything through the center portion of the eye.
Two types of this ocular disease exist. First, wet macular degeneration means that abnormal blood vessels that are located behind the retina grow under the macular. Along with leaking blood and fluid, this leads to scarring and, sometimes, permanent damage. Second, dry macular degeneration progresses slowly as part of the natural aging process. Typically, it affects both eyes at some point.
Cataracts
Roughly 20 million people in the U.S. over the age of 40 have cataracts in either one or both eyes. While they can develop in children, teens, and young adults, cataracts are most often associated with age. With this, a film covers the eye, which, in turn, makes everything appear blurry.
Of all the different kinds of ocular diseases that lead to blindness worldwide, cataracts rank number two. Fortunately, an eye doctor can remove the damaged lens, followed by implanting an artificial one. After recovery, patients see amazingly well.
Diabetic Retinopathy
If you have diabetes, then you’re at risk of developing this ocular disease. This particular disease causes progressive damage to the retina’s blood vessels. The first stage consists of mild non-proliferative retinopathy and then moderate non-proliferative retinopathy, which blocks some of the vessels.
Then, it moves into stage three or severe non-proliferative retinopathy, which means more blood vessels become blocked. The fourth and final state, proliferative retinopathy, is the most advanced. Although Diabetic Retinopathy does affect just one eye on occasion, it typically involves both eyes.
Start by improving your overall health. Eat balanced meals, keep your blood pressure and cholesterol levels down, and take insulin. In addition, regular exercise, losing weight, and giving up smoking all make a huge difference. From there, a qualified eye doctor can provide you with treatment options to reduce the risk of losing your vision.
Glaucoma
Many people think glaucoma is one type of ocular disease. However, it’s a group of diseases that cause damage to the optic nerve. When that happens, people face the risk of losing their sight completely. With glaucoma, the fluid pressure inside the eyes gradually rises.
There are also two categories of glaucoma: open-angle and closed-angle. Not only is open-angle glaucoma chronic, but it also progresses slowly. Often, a person can have this type without knowing it. Unfortunately, they don’t realize there’s an issue until they have a comprehensive eye exam performed.
As for closed-angle glaucoma, it’s usually painful and it comes on suddenly. In addition, an individual can lose their vision much faster with this kind of glaucoma compared to the open-angle kind. Because this happens fast and involves pain, it’s diagnosed much quicker as well.
For these common types of ocular diseases, it’s important to have your vision checked. An eye doctor might simply diagnose you with myopia or hyperopia, followed by prescribing either eyeglasses or contact lenses. If an ocular disease is diagnosed, the optometrist will determine the best treatment plan for optimal eye health and vision.
iLux
If you have dry eye syndrome, you understand the frustration of repeatedly applying eye drops and other therapies in vain. The iLux®, a new product on the market, may help address your problem.
It treats dry eye syndrome by combining heat and pressure to clear obstructions from the meibomian glands. Learning how it works and its advantages in treating dry eyes may help you.
What Is iLux?
Millions of individuals worldwide suffer from the prevalent ailment known as dry eye syndrome. This happens when your eyes do not produce tears in sufficient amounts or when tears evaporate too soon. Discomfort, irritability, and even eyesight issues may result from this. Although several treatments for dry eyes exist, many are transient and call for repeated application.
iLux is a medical device designed to treat dry eye syndrome. It combines heat and pressure to remove blockages from the meibomian glands. These glands in the eyelids produce the oil that prevents your tears from evaporating too quickly.
The handheld device is easy to use, making it a convenient and effective solution for those who suffer from dry eyes. It is a practical choice for people with busy schedules because no downtime or recovery period is necessary.
How Does It Work?
The device works by applying gentle heat and pressure to the eyelids. This helps loosen and remove blockages from the meibomian glands. The treatment allows the glands to function properly, producing the necessary oils to keep the eyes moisturized and healthy. The device also provides targeted treatment to specific areas of the eyelids. This allows for a more customized and effective treatment experience.
Benefits
Using this medical device to treat dry eyes offers numerous benefits, including:
Improved Comfort
Dry eyes can cause discomfort, irritation, and even pain. By treating dry eyes with iLux, you can experience improved comfort and reduced symptoms.
Enhanced Vision
Dry eye syndrome can affect vision, causing blurriness or difficulty focusing. Treating the condition with iLux can help improve vision and clarity.
Noninvasive
Unlike other treatments for dry eyes, such as surgery, iLux is a noninvasive solution that requires no downtime or recovery period.
How to Use the Device
Using iLux to treat dry eyes is straightforward. Since it is handheld and portable, this device is easy to use at home and when traveling.
To use it, follow these steps:
To determine if it is a good fit for you and to get usage instructions, consult your eye doctor.
Position the device against your closed eyelid over the affected area.
It will apply gentle heat and pressure to the eyelid, helping remove blockages from the meibomian glands.
Repeat this process on each eyelid as instructed by your doctor.
After using it, you may experience some mild discomfort or redness in the treated area. These are usually not severe; they should go away within a day or two.
Conclusion
If you are experiencing dry eyes, the iLux might be the solution for you. This noninvasive medical device uses heat and pressure to remove blockages from the meibomian glands. The treatment allows for improved eye health and comfort. To learn more about the device and whether it is right, consult your eye doctor today.